Largest Public Blockchains
The purpose of public blockchains is to provide a secure and transparent digital record of transactions that is distributed across a network of computers. They are immutable and virtually incorruptible, making them ideal for securely storing and transferring data. This can be used for a variety of applications, from tracking asset ownership to creating digital currencies.
This article goes over the key characteristic of Bitcoin, Ethereum and Cardano blockchains
Table of Content
Bitcoin
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital form of cash. But unlike the fiat currencies, you’re used to, there is no central bank controlling it. Instead, the financial system in Bitcoin is run by thousands of computers distributed around the world. Anyone can participate in the ecosystem by downloading open-source software.
What is Bitcoin used for?
Many appreciate it for its permissionless nature – anyone with an Internet connection can send and receive it. It’s a bit like cash in that no one can stop you from using it, but its digital presence means that it can be transferred globally.
What makes Bitcoin valuable?
Bitcoin is decentralized, censorship-resistant, secure, and borderless.
This quality has made it appealing for use cases such as international remittance and payments where individuals don’t want to reveal their identities (as they would with a debit or credit card).
Bitcoin has been nicknamed digital gold, due to a finite supply of coins available. Some investors view Bitcoin as a store of value. Because it’s scarce and difficult to produce, it has been likened to precious metals like gold or silver.
Holders believe that these traits – combined with global availability and high liquidity – make it an ideal medium for storing wealth in for long periods. They believe that Bitcoin’s value will continue to appreciate over time.
Is Bitcoin legal?
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are legal in most countries. There are a handful of exceptions, though.
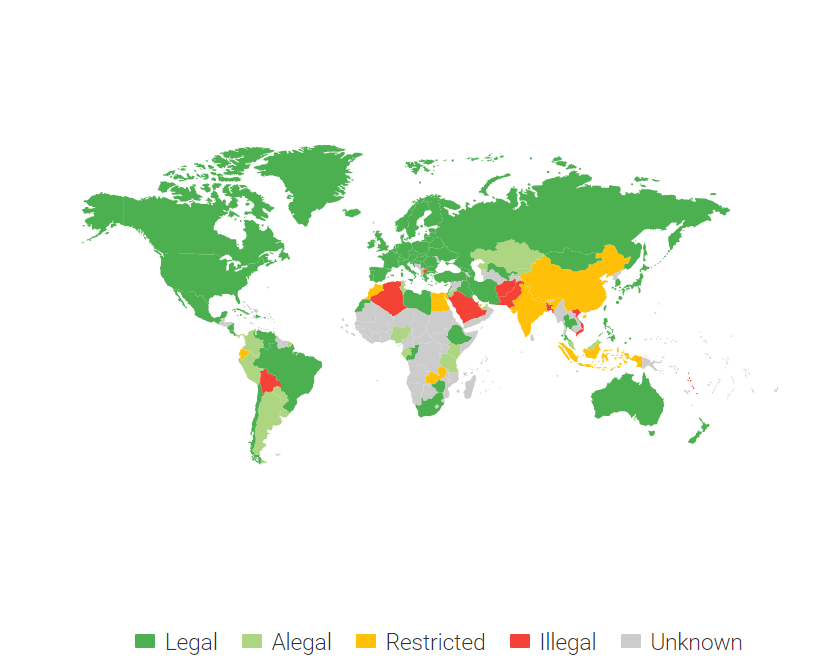
Countries where Bitcoin is Banned
Algeria - Arguing that they are not backed by anything physical, Algeria has banned cryptocurrencies.
Bolivia - The Central Bank has prohibited the use of cryptocurrencies because of their unregulated nature.
Bangladesh - Citing possibilities for money laundering and being unauthorized by the Bangladesh bank, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are illegal.
Dominican Republic - Citing that they are not legal tender, cryptocurrencies are illegal in the Dominican Republic.
Ghana - Although cryptocurrencies are regarded as illegal in Ghana, the Bank of Ghana sees blockchains potential and is assessing how to fit them into their financial structure.
Nepal - Nepal's central bank has banned Bitcoin because it is not a legal currency.
The Republic of Macedonia - Citizens are warned that they cannot have crypto securities abroad. Crypto is still illegal.
Qatar - Citing price volatility, the possibility of financial crimes, and lack of central government support, cryptocurrency activity is banned
Countries where Bitcoin is Restricted
countries where Bitcoin is somewhat restricted and cannot be traded or used for payment. In such states, banks and other financial service providers are prohibited from dealing with cryptocurrency exchanges and companies, and in more extreme cases the countries have even banned crypto exchanges.
Bahrain - You need a license in order to use crypto-asset services in Bahrain.
China - China's digital Yuan has issued on-chain wages, a first for the country. Although having researched cryptocurrencies for many years, China is treading cautiously in the market, listing a whole gamut of rules in terms of restricting Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). China had the resources to operate with 70% of Bitcoin mining facilities, but that has been regulated by officials for environmental reasons.
Hong Kong - A law may be enacted that might restrict crypto trading to individuals who have over $1 million in their investment portfolio. Other than this, Hong Kong emphasizes certain regulations when it comes to ICOs. Exchanges also need regulations in order to be enacted.
Iran - Financial institutions are not permitted to handle cryptocurrencies.
Kazakhstan - There are heavy cryptocurrency restrictions by the National Bank with exchanges and mining banned. A complete ban of cryptocurrency has been contemplated.
Russia - Crypto is legal in Russia but is restricted. Banks and exchanges have to be registered by the Central Bank and crypto cannot be used as a payment method.
Saudi Arabia - Once banned, Bitcoin is now legal in the country. Banks, however, are banned from participating.
Turkey - Cryptocurrencies are not allowed as financial assets in banks. They also cannot be classified as payment tools.
Vietnam - Although Bitcoin is still prohibited in trade relations by the State Bank, possession and trade in crypto is a tolerated occurrence for the average user. Research in the country is being done to further understand cryptocurrency and its implications
Countries Where Bitcoin is Official Legal Tender
El Salvador - in June 2021, El Salvador becomes first country to adopt bitcoin as legal tender. This means that prices from that date onwards could be shown in bitcoin, tax contributions could be paid with the digital currency, and exchanges in bitcoin would not be subject to capital gains tax.
The Central African Republic - in April 2022 the Central African Republic lawmakers voted unanimously to pass a bill legalizing crypto. Bitcoin will be considered legal tender alongside the regional Central African CFA franc.
Who created Bitcoin?
Satoshi Nakamoto is the pseudonym behind the development of Bitcoin and the authorship of the original Bitcoin whitepaper. The question "who is Satoshi Nakamoto?" has led to speculation about their true identity and people falsely claiming they are Satoshi Nakamoto.
Satoshi didn't invent blockchain, but he was the first to create a decentralized currency based on blockchain technology.
Before Satoshi cut off all communications in April 2011, they claimed to be male, Japanese and born on April 5, 1975. However, people have observed that Satoshi's command of English was so high that they're likely to be from a native-English speaking country. Also, their communications mainly occurred during European working hours, so it's speculated they didn't reside in Japan.
What was before Bitcoin?
Bitcoin actually combines a number of existing technologies that had been around for some time. This concept of a chain of blocks wasn’t born with Bitcoin. The use of unalterable data structures like this can be traced back to the early 90s when Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta proposed a system for timestamping documents. Much like the blockchains of today, it relied on cryptographic techniques to secure data and to prevent it from being tampered with.
How are new Bitcoins created?
Bitcoin has a finite supply, but not all units are in circulation yet. The only way to create new coins is through a process called mining – the special mechanism for adding data to the blockchain.
The circulating supply of Bitcoin will gradually increase until the max supply of 21 million coins is reached.
How does Bitcoin Mining work?
By mining, participants add blocks to the blockchain. To do so, they must dedicate computing power to solving a cryptographic puzzle. As an incentive, there is a reward available to whoever proposes a valid block.
It’s expensive to generate a block, but cheap to check if it’s valid. If someone tries to cheat with an invalid block, the network immediately rejects it, and the miner will be unable to recoup the mining costs.
The reward – often labeled the block reward – is made up of two components: fees attached to the transactions and the block subsidy. The block subsidy is the only source of “fresh” bitcoins. With every block mined, it adds a set amount of coins to the total supply.
How long does it take to mine a block?
The protocol adjusts the difficulty of mining so that it takes approximately ten minutes to find a new block. Blocks aren’t always found exactly ten minutes after the previous one – the time taken merely fluctuates around this target.
Can I revert Bitcoin transactions?
Once data is added to the blockchain, it’s not easy to remove it (in practice, it’s virtually impossible). This means that when you make a transaction, it can’t be undone.
Can I make money with Bitcoin?
Lending is a popular form of passive income. By lending your coins to someone else, you can generate interest that they will pay out at a later date. Providing liquidity to a Decentralized Exchange is also a popular strategy.
There is no Staking with Bitcoin
Is Bitcoin anonymous?
Not really. Bitcoin might seem anonymous initially, but this isn’t correct. The Bitcoin blockchain is public and anyone can see the transactions. Your identity isn’t tied to your wallet addresses on the blockchain, but an observer with the right resources could potentially link the two together. It’s more accurate to describe Bitcoin as pseudonymous. Bitcoin addresses are viewable to everybody, but the names of their owners are not.
That said, the system is relatively private, and there are methods to make it even harder for observers to figure out what you’re doing with your bitcoins. Freely available technologies can create plausible deniability to “break the link” between addresses.
How many transactions can Bitcoin process?
Based on the average number of transactions per block, Bitcoin can manage approximately five transactions per second at the moment. It’s much lower than that of centralized payment solutions, but this is one of the costs of a decentralized currency.
Because it’s not managed by a data center that a single entity can upgrade at will, Bitcoin must limit the size of its blocks. A new block size that allows 10,000 transactions per second could be integrated, but it would harm the network’s decentralization. Remember that full nodes need to download new information roughly every ten minutes. If it becomes too burdensome for them to do so, they’ll likely go offline.
What is a Bitcoin node?
“Bitcoin node” is a term used to describe a program that interacts with the Bitcoin network in some way. It can be anything from a mobile phone operating a Bitcoin wallet to a dedicated computer that stores a full copy of the blockchain.
What is a Bitcoin Full node?
A full node validates transactions and blocks if they meet certain requirements (i.e., follow the rules). Most full nodes run the Bitcoin Core software, which is the reference implementation of the Bitcoin protocol.
Full nodes are integral to Bitcoin’s decentralization. They download and validate blocks and transactions, and propagate them to the rest of the network. Because they independently verify the authenticity of the information they’re being provided with, the user doesn’t rely on a third party for anything.
What is a Bitcoin Light node?
Light nodes are not as capable as full nodes, but they’re also less resource-intensive. They allow users to interface with the network without performing all of the operations that a full node does.
Where a full node downloads all blocks to validate them, light nodes only download a portion of each block (called a block header). Though the block header is tiny in size, it contains information that allows users to check that their transactions are in a specific block.
Light nodes are ideal for devices with constraints in bandwidth or space. It’s common to see this type of node being used in desktop and mobile wallets. Because they can’t perform validation, however, light nodes are dependent on full nodes.
What is a Bitcoin Full node?
Mining nodes are full nodes that perform an additional task – they produce blocks. As we touched on earlier, they require specialized equipment and software to add data to the blockchain.
Mining nodes take pending transactions and hash them along with other information to generate a number. If the number falls below a target set by the protocol, the block is valid and can be broadcast to other full nodes.
But in order to mine without relying on anyone else, miners need to run a full node. Otherwise, they can’t know what transactions to include in the block.
If a participant wants to mine but doesn’t want to use a full node, they can connect to a server that gives them the information they need. If you mine in a pool (that is, by working with others), only one person needs to run a full node.
How long does it take to mine a bitcoin?
It’s difficult to give a one-size-fits-all answer because there are a number of variables to consider. How quickly you can mine a coin depends on the amount of electricity and hash rate available to you. You’ll also need to factor in the costs of actually operating a mining device.
Ethereum
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a technology for building apps and organizations, holding assets, transacting and communicating without being controlled by a central authority. There is no need to hand over all your personal details to use Ethereum - you keep control of your own data and what is being shared. Ethereum has its own cryptocurrency, Ether, or ETH for short, which is used to pay for certain activities on the Ethereum network.
While Bitcoin is only a payment network, Ethereum is more like a marketplace of financial services, games, social networks and other apps that respect your privacy and cannot censor you.
What is Ethereum Used for?
Ethereum can be used by anyone to create any secured digital technology. It has a token designed for use in the blockchain network, but it can also be used by participants as a method to pay for work done on the blockchain.
Ethereum is described by the organization as “the world’s programmable blockchain,” positioning itself as an electronic, programmable network with many applications. It is a platform that supports smart contracts. The Bitcoin blockchain, by contrast, was created only to support the bitcoin cryptocurrency.
The Ethereum platform was founded with broad ambitions to leverage blockchain technology for many diverse applications. Bitcoin was designed strictly as a payment method.
Ethereum enables the deployment of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) to be built and run without any downtime, fraud, control, or interference from a third party. Ethereum comes complete with its own programming language that runs on a blockchain, enabling developers to build and run distributed applications.
The potential applications of Ethereum are wide-ranging and are powered by its native cryptographic token, ether (commonly abbreviated as ETH). In 2014, Ethereum launched a presale for ether, which received an overwhelming response. Ether is like the fuel for running commands on the Ethereum platform and is used by developers to build and run applications on the platform.
What makes Ethereum valuable?
The Ethereum network has become a staple in the crypto space over the years, with many projects based on it. A large number of initial coin offerings used Ethereum in 2017 as a funding vehicle. Crypto assets based on Ethereum’s blockchain are called ERC-20 tokens, although ERC-721 tokens also exist as nonfungible (NFT) tokens built on the network.
When a project builds on Ethereum, it may come with an asset for use within that ecosystem. That asset would likely be an ERC-20 token. It is not uncommon, however, for projects to switch over to their own mainnet blockchain after launching initially on Ethereum’s blockchain.
Much of the decentralized finance sector of crypto also began on Ethereum, with decentralized exchanges based on Ethereum’s blockchain hosting trading for numerous tokens associated with the niche. DeFi lets participants borrow and lend crypto assets, among other capabilities.
Is Ethereum Legal?
Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies are legal in most countries. There are a handful of exceptions, though. The legality of Ether and other cryptocurrencies follows that of Bitcoin as the regulators in most countries put them in the same category. For a list of countries refer to the same section on Bitcoin
In the US, which is the largest crypto market, the regulators (SEC) distinguish between something that is an "investment contract" (sometimes also referred to as a security) and something that is not an investment contract.
A host of implications are raised if the SEC determines a cryptocurrency, or a token to be a security. Effectively, it means the SEC can determine whether or not a token can be sold to U.S. investors and compels the project to register with the SEC.
To determine if something is a security the regulators use a so-called "Howey Test"
A significant application of the Howey Test came in 2017 when the SEC ruled that the sale of DAO tokens in exchange for Ether violated federal securities law. Instead of taking enforcement action, the SEC warned that securities laws applied to token sales—effectively firing a warning shot at the cryptocurrency industry.
Because of the Howey Test, most ICOs that take place today are likely to be off-limits to U.S investors.
In regards to Bitcoin. In June 2018, the former Chair of the SEC, Jay Clayton, clarified that bitcoin is not a security: "Cryptocurrencies: These are replacements for sovereign currencies, replace the dollar, the euro, the yen with bitcoin. That type of currency is not a security," said Clayton. Bitcoin, which has never sought public funds to develop its technology, does not pass the Howey Test used by the SEC to classify securities.
Who created Ethereum?
Ethereum was created by a Russian-Canadian programmer named Vitalik Buterin. Buterin first became interested in blockchain technology in 2011, when he discovered the Bitcoin whitepaper, and he began working on his own blockchain project shortly thereafter.
In 2013, Buterin co-founded Bitcoin Magazine, a publication focused on Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, and began developing the initial concept for Ethereum. The following year, he released a whitepaper outlining his vision for a decentralized blockchain platform that could support a wide range of decentralized applications (dapps) and smart contracts.
In 2014, Buterin founded the Ethereum Foundation, a non-profit organization dedicated to promoting the development and adoption of the Ethereum platform. The foundation conducted an initial coin offering (ICO) later that year to raise funds for the continued development of the platform, which was a major success, raising over $18 million in just a few weeks.
Since then, Ethereum has become one of the most popular and widely used blockchain platforms in the world, with a thriving ecosystem of developers, entrepreneurs, and users building and using decentralized applications and services on the network. Buterin continues to play an active role in the development and evolution of Ethereum, working closely with the Ethereum Foundation and other stakeholders to guide the platform's future direction.
What was before Ethereum?
Before Ethereum, there were several blockchain projects that laid the foundation for the development of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dapps).
The first popular blockchain was Bitcoin, initially used solely to facilitate user transactions.
As the blockchain community continued to develop and experiment with new use cases for blockchain technology, other projects emerged that built upon the basic blockchain architecture established by Bitcoin. These projects included Namecoin, a blockchain-based domain name registry system, and Mastercoin, which introduced the concept of smart contracts to the blockchain ecosystem.
Another important project that preceded Ethereum was Ripple, which was developed in 2012 by a team of entrepreneurs and developers led by Chris Larsen and Jed McCaleb. Ripple was designed as a decentralized payment protocol that could be used to facilitate cross-border transactions and money transfers between individuals and institutions.
Despite the early success of these projects, they were limited in their ability to support complex smart contracts and dapps due to the relatively simple scripting language used in their blockchain protocols. Ethereum was created as a way to address these limitations and provide a more flexible and versatile platform for building decentralized applications and executing smart contracts.
How are new Ethereums created?
New Ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network, is created through a process called mining. Up until April 2023, Ethereum used a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW) to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain.
Miners used powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems in order to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. This process required a significant amount of computational power, electricity, and specialized hardware.
When a miner successfully added a new block to the blockchain, they were rewarded with a certain amount of Ether as an incentive for their work. The amount of Ether rewarded for each block decreases over time, as the total supply of Ether approaches its maximum limit.
In April 2023, Ethereum transitioned to a new consensus mechanism called Proof of Stake (PoS), which replaced the current mining process with a more energy-efficient and scalable approach. Under PoS, validators called "stakers" lock up a certain amount of Ether as collateral and be selected to validate transactions and add new blocks based on their stake. Stakers earn rewards in the form of transaction fees instead of block rewards.
How does Ethereum mining work?
In the Ethereum's Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism, validators, also called "stakers," are selected to add new blocks to the blockchain based on the amount of Ether they hold and have locked up as collateral. This process is called "staking."
Validators who wish to participate in staking must first lock up a certain amount of Ether as collateral, which is called a "stake." This stake serves as a security deposit, as validators risk losing their stake if they behave maliciously or fail to perform their duties properly.
When it's time to add a new block to the blockchain, a set of validators are selected at random to validate and confirm transactions. The number of validators selected and the probability of being selected is proportional to the size of their stake. Validators are incentivized to perform their duties honestly and efficiently, as they stand to earn rewards in the form of transaction fees for adding a block and verifying transactions.
If a validator behaves maliciously or fails to perform their duties properly, they risk losing their stake. This is achieved through a process called "slashing," in which a portion of the validator's stake is confiscated as a penalty. For example, if a validator signs off on an invalid transaction, their stake may be slashed as punishment.
In addition to being more energy-efficient and scalable than PoW, PoS is designed to be more secure against certain types of attacks, such as 51% attacks, where a malicious actor controls a majority of the mining power and can manipulate the blockchain. PoS also has the potential to reduce centralization in the mining process, as staking requires less specialized hardware than PoW mining, making it more accessible to a wider range of users.
How long does it take to mine a block?
In Ethereum's Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism new blocks are added to the blockchain approximately every 12 seconds. Validators who successfully validate a block are rewarded with Ether (ETH) as a form of incentive, with the exact amount depending on several factors such as the number of validators and the total amount of ETH staked in the network.
Can I revert Ethereum transactions?
In general, Ethereum transactions cannot be reverted or cancelled once they are confirmed and added to the blockchain. This is because the Ethereum network is designed to be decentralized and immutable, meaning that transactions are recorded permanently and cannot be altered or deleted.
However, there are some cases where transactions can be reversed or cancelled. For example, if a transaction is sent with a higher fee than necessary, it may be possible to cancel the original transaction and send a new one with a lower fee. Additionally, if a transaction is sent to the wrong address or contains an error, it may be possible to recover the funds by contacting the recipient and requesting a refund.
It's important to note that these methods are not guaranteed to work and should only be attempted in certain situations. In general, it's best to double-check all transaction details before sending and to use caution when sending large amounts of cryptocurrency.
Can I make money with Ethereum?
With the transition to Ethereum Proof of Stake (PoS), users can now earn rewards by staking their ETH to help secure the network. Staking involves holding a certain amount of ETH and using it to validate transactions in exchange for earning a portion of the rewards earned by the network.
Ethereum is the foundation of many DeFi protocols and applications. Users can participate in DeFi by lending, borrowing, trading, and providing liquidity, among other activities. By participating in these activities, users can earn interest, fees, and other rewards.
It's important to note that investing in Ethereum and participating in these activities involves risk, and users should carefully consider their investment goals and risk tolerance before getting involved.
Is Ethereum anonymous?
Ethereum transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, meaning anyone can see the transaction details such as the sender and receiver addresses and the amount of Ethereum transferred. However, the identities of the individuals or entities behind these addresses are not directly visible on the blockchain.
How many transactions can Ethereum process?
The current version of Ethereum, can process around 15 transactions per second (TPS)
What is an Ethereum node?
An Ethereum node is a computer or server that participates in the Ethereum network by maintaining a copy of the entire Ethereum blockchain. Nodes help to validate transactions, propagate them to other nodes, and add new blocks to the blockchain.
There are several types of Ethereum nodes, including full nodes, light nodes, and archive nodes.
Running an Ethereum node requires a significant amount of storage, processing power, and bandwidth, as the blockchain is constantly growing and updating. However, by running a node, users can help to support the Ethereum network, improve its security and decentralization, and potentially earn rewards by staking their Ethereum.
What is an Ethereum Full node?
Full nodes store a complete copy of the blockchain and are required to validate and process transactions.
What is an Ethereum Light node?
Light nodes, on the other hand, only store a subset of the blockchain and rely on full nodes to verify transactions.
What is an Ethereum Archive node?
Archive nodes are similar to full nodes, but they also store all historical data of the blockchain, which allows them to provide more detailed information about past transactions.
How long does it take to mine an Ethereum?
Blocks on Ethereum are produced about 12 seconds apart
Cardano
What is Cardano?
Cardano is a proof-of-stake blockchain platform: the first to be founded on peer-reviewed research and developed through evidence-based methods. It combines pioneering technologies to provide unparalleled security and sustainability to decentralized applications, systems, and societies.
Cardano’s focus has been on creating a system that is cheaper to use and more efficient than Ethereum.
What is Cardano Used for?
Cardano is a third-generation blockchain platform that was created to address some of the issues faced by earlier blockchains such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. The platform is primarily used for decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts, similar to other popular blockchain platforms.
One of the key features of Cardano is its focus on scientific research and peer-reviewed development. This approach aims to create a blockchain that is more secure, scalable, and sustainable than its predecessors. Cardano is also known for its use of a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, which enables faster transaction times and lower energy consumption compared to the proof-of-work mechanism used by Bitcoin.
Here are some of the main use cases for the Cardano blockchain:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Cardano aims to become a leading platform for DeFi applications, with a focus on creating a more secure and scalable ecosystem. Some of the DeFi applications being developed on Cardano include lending and borrowing platforms, decentralized exchanges, and stablecoins.
- Identity and Authentication: Cardano is exploring the use of blockchain technology for identity and authentication purposes. The platform aims to create a secure and decentralized identity system that can be used for a variety of purposes, including voting, accessing healthcare services, and financial transactions.
- Supply Chain Management: The transparent and secure nature of blockchain technology makes it well-suited for supply chain management. Cardano is exploring the use of blockchain to create a more efficient and secure supply chain ecosystem, with applications such as tracking the origin and authenticity of products and ensuring fair trade practices.
- Gaming and Entertainment: Cardano is also exploring the use of blockchain technology for gaming and entertainment applications. These applications can include digital collectibles, virtual worlds, and decentralized gaming platforms.
- Social Impact: Cardano is also exploring the use of blockchain technology for social impact initiatives, such as creating a decentralized platform for philanthropic giving, tracking charitable donations, and enabling microfinance initiatives.
Overall, the Cardano blockchain is being used for a wide range of applications, with a focus on creating a more secure, scalable, and sustainable blockchain ecosystem. As the platform continues to evolve, we can expect to see more innovative applications being developed on the Cardano blockchain.
What makes Cardano valuable?
Cardano is a valuable blockchain platform due to several unique features that set it apart from other blockchains. Here are some of the key factors that contribute to Cardano's value:
- Scientific approach: Cardano's development is based on a rigorous scientific approach. The platform's design and development are peer-reviewed by leading academics and researchers in the blockchain space, ensuring that the platform is reliable, secure, and innovative.
- Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism: Cardano uses a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, which is more energy-efficient and faster than the proof-of-work mechanism used by Bitcoin. This makes the platform more scalable and sustainable, with lower transaction fees and faster transaction times.
- Interoperability: Cardano is designed to be interoperable with other blockchain platforms and traditional financial systems, making it easier for businesses and individuals to use and adopt.
- Smart contract functionality: Cardano's smart contract functionality is being developed in a way that addresses the limitations of other blockchain platforms. The platform's smart contracts are designed to be more secure, flexible, and scalable, enabling a wider range of decentralized applications and use cases.
- Community-driven governance: Cardano's governance is based on a community-driven approach. The platform's governance model allows for community members to propose and vote on changes to the network, ensuring that the platform evolves in a way that is aligned with the interests of its users.
Overall, Cardano's combination of scientific rigor, innovative technology, and community-driven governance make it a valuable blockchain platform with a promising future. The platform's focus on sustainability, scalability, and security also makes it well-suited for a wide range of applications, including decentralized finance, supply chain management, identity and authentication, gaming and entertainment, and social impact initiatives. As the platform continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases and applications being developed on the Cardano blockchain.
Is Cardano Legal?
Cardano, like other blockchain platforms, is a decentralized network that operates outside of traditional legal and regulatory frameworks. However, the use of Cardano and other blockchain platforms is generally legal, provided that users comply with relevant laws and regulations in their respective jurisdictions.
In some countries, the legal status of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology is still uncertain, and regulatory frameworks are still being developed. However, in many jurisdictions, cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology are subject to existing laws and regulations, such as those related to financial services, securities, and taxation.
The Cardano Foundation, which is responsible for the development and promotion of the Cardano blockchain, has taken steps to ensure that the platform is compliant with relevant laws and regulations. The Foundation has also engaged with regulators and policymakers to promote the development of clear and effective regulatory frameworks for blockchain technology.
Who created Cardano?
Cardano was created by Charles Hoskinson, a co-founder of Ethereum and the founder of IOHK (Input Output Hong Kong). Hoskinson began developing Cardano in 2015 to create a more secure, scalable, and sustainable blockchain platform.
IOHK is a blockchain research and development company dedicated to building decentralized systems and providing blockchain solutions for organizations and individuals. IOHK is also one of the main companies developing and maintaining the Cardano blockchain.
What was before Cardano?
Before Cardano, Charles Hoskinson was involved in the development of Ethereum, another blockchain platform. Hoskinson was one of the original co-founders of Ethereum, along with Vitalik Buterin and others.
Hoskinson played a key role in the early development of Ethereum, helping to create the platform's initial architecture and design. However, he left the project in 2014 over disagreements with other members of the Ethereum team.
After leaving Ethereum, Hoskinson founded IOHK and began work on Cardano. He saw an opportunity to create a new blockchain platform that would address some of the limitations and challenges of existing blockchain technologies.
Cardano was launched in 2017, after several years of development and testing. Since its launch, the platform has gained a significant following and has become one of the most popular and widely-used blockchain platforms in the world
How is the new ADA created?
The new ADA is created through a process called "minting" or "forging", which is similar to the process of "mining" used by other blockchain platforms like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
In the Cardano network, new ADA is created as a reward for the validators who participate in the process of adding new blocks to the blockchain. Validators are also known as "stakers" in the Cardano network, and they are responsible for securing the network and verifying transactions.
When a validator successfully creates a new block and adds it to the Cardano blockchain, they receive a reward in the form of newly-minted ADA. The amount of ADA minted per block is determined by the Cardano protocol, and it is designed to gradually decrease over time, resulting in a fixed maximum supply of 45 billion ADA.
The minting process in Cardano is designed to be energy-efficient and sustainable, using a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism that does not require the same level of computational resources as the proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism used by Bitcoin and other blockchain platforms. This makes Cardano a more environmentally-friendly blockchain platform and reduces the cost of participating in the network.
Overall, the minting process in Cardano is designed to be fair, secure, and sustainable, with rewards distributed to validators who contribute to the network's overall security and stability.
How does Cardano mining work?
Cardano uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, rather than the proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism used by Bitcoin and some other blockchain platforms. As a result, there is no traditional mining process in Cardano.
Instead of mining, the Cardano network uses a process called "staking", which allows users to participate in the network and earn rewards for helping to secure the blockchain.
Staking in Cardano involves locking up a certain amount of ADA tokens as a "stake" in the network. This stake serves as a validator's collateral and gives them the right to participate in the network and add new blocks to the blockchain.
Validators are selected to add new blocks based on the size of their stake, with larger stakes resulting in a higher chance of being selected to create a new block. When a validator is selected to add a new block to the blockchain, they earn a reward in the form of newly-minted ADA.
The amount of ADA that can be earned through staking depends on a variety of factors, including the size of the validator's stake and the current network conditions. The Cardano protocol also includes mechanisms to encourage users to delegate their stake to larger pools, which helps to distribute rewards more evenly and improve the overall security and decentralization of the network.
Overall, staking in Cardano serves a similar function to mining in other blockchain platforms, allowing users to participate in the network and earn rewards for helping to secure and maintain the blockchain. However, the use of a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism allows for a more energy-efficient and sustainable approach to network validation, which is a key advantage of the Cardano platform.
How long does it take to mine a block?
In Cardano's PoS mechanism, blocks are created by validators who participate in the network by staking their ADA tokens. The chance of a validator being selected to create a new block depends on the size of their stake relative to the total amount of ADA being staked on the network.
Cardano's protocol is designed to produce an average of one block per 20 slot, with each slot lasting about 1 second. So on average every 20 seconds, sometimes more and sometimes less as a block can be at the beginning or the end of each of thee 20 slot intervals.
Can I revert Cardano transactions?
Once a transaction has been broadcast to the Cardano network and added to a block in the blockchain, it becomes a permanent part of the ledger and cannot be modified or deleted. This is an intentional design feature of the Cardano blockchain, as it helps to ensure the integrity and security of the network.
Can I make money with Cardano?
It is possible to make money with the Cardano blockchain, but like any investment or financial activity, it carries risks and requires careful consideration.
One way to potentially earn money with Cardano is through investing in the ADA cryptocurrency. Like other cryptocurrencies, the value of ADA can fluctuate based on market demand, supply, and other factors. If the value of ADA increases over time, an investor who buys ADA at a lower price and sells it at a higher price could potentially earn a profit.
Another way to potentially earn money with Cardano is by participating in the network as a validator. Validators in the Cardano network can earn rewards in ADA for staking their tokens and helping to secure the network. However, becoming a validator typically requires a significant investment of time and resources, as well as technical expertise and knowledge of the Cardano protocol.
Finally, there may be opportunities to earn money through various projects and applications built on top of the Cardano blockchain, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, gaming applications, or other dApps (decentralized applications). However, like any investment or financial activity, it is important to carefully evaluate the risks and potential rewards of any opportunity and make informed decisions based on one's own risk tolerance and financial goals.
Is Cardano anonymous?
The Cardano blockchain is not anonymous, but it does include certain features that can help to protect user privacy.
Like most blockchain networks, the Cardano ledger is public, which means that all transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be viewed by anyone with access to the network.
How many transactions can Cardano process?
Cardano uses a different model, which allows it to send multiple "transactions" in each transaction. This is possible by adopting the eUTXO model. This is therefore not comparable with the transactions per second (TPS) metric which is often used to compare throughput of networks
What is a Cardano node?
A node is a participant in the network that maintains a complete copy of the blockchain ledger and facilitates the validation and propagation of transactions and blocks.
In simple terms, a node is a computer or server that runs software specifically designed to communicate with other nodes on the Cardano network and participate in the consensus mechanism that secures and maintains the network. Each node on the network is responsible for verifying the validity of new transactions and blocks, and helping to propagate this information to other nodes so that they can be added to the blockchain.
There are several types of nodes that can participate in the Cardano network, including:
- Core nodes
- Relay (or Edge) nodes
Overall, nodes are a critical component of the Cardano blockchain, providing the computational resources and network infrastructure necessary to maintain a secure, decentralized, and reliable blockchain network.
What is a Cardano Full node?
These nodes are responsible for participating in the consensus mechanism that determines the valid state of the blockchain. Core nodes are involved in the process of block creation and validation, and they help to maintain the integrity and security of the network.
What is a Cardano Relay node?
These nodes are responsible for relaying transactions and blocks between other nodes on the network, helping to ensure that new information is quickly and efficiently propagated across the network. They also provide access to the various services and applications built on the network.
Other
There are several other large and notable blockchains besides Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Cardano. Here are a few examples with a short description of each:
Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
BSC is a blockchain developed by the popular cryptocurrency exchange Binance. It is a high-performance blockchain that supports smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps), making it a direct competitor to Ethereum. BSC's key feature is its low transaction fees, which makes it an attractive alternative to Ethereum for developers and users alike.
Solana (SOL)
Solana is a fast blockchain designed for high-speed transactions and smart contracts. Its key feature is its high throughput, which enables it to process up to 65,000 transactions per second, making it one of the fastest blockchains in the world. This makes it ideal for decentralized applications that require fast and secure transactions.
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot is a blockchain designed to connect multiple blockchains together, enabling them to share data and communicate with each other. It is a multi-chain network that allows for interoperability between different blockchains, making it easier for developers to build decentralized applications that can access data and functionality from multiple blockchains.
Avalanche (AVAX)
Avalanche is a blockchain that aims to provide high performance, scalability, and security. Its key feature is its consensus mechanism, which uses a combination of proof-of-stake (PoS) and Byzantine fault tolerance (BFT) to achieve consensus. This makes it highly scalable and secure, while also being energy-efficient.
Each of these blockchains has its own unique features and strengths, and they are all working towards advancing the technology and adoption of blockchain in various ways.
References
Global Bitcoin Political Support & Public Opinion - Coin Dance
Legality of cryptocurrency by country or territory - Wikipedia
Countries Where Bitcoin Is Banned or Legal In 2022 - Crypto News
Cryptocurrency Legal Status by Country - money.com
Central African Republic becomes second country to adopt bitcoin as legal tender - CNBC
Who Created Ethereum - Coin Desk
What is Cardano - Investopedia
License
This work is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) The license allows you to copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format, as well as remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, including commercial, as long as you give appropriate credit to the creator.